What is Open Banking?
Open Banking or Open Bank Data is a revolutionary practice that is poised to reshape the banking industry. It provides third-party financial service providers with open access to consumer banking, transaction, and other financial data from banking institutions and non-banking financial entities via. (API) Application Programming Interface. The data may be used to create new applications that facilitate development of finance management tools, comparison tools, etc.
Why do we need Open Banking?
Consumer Payment Information is highly sensitive to be shared with a third-party. So, how does Open Banking help the consumer and why do we need it? Which problem statements are being resolved using the revolutionary concept of Open Banking? We attempt to answer these critical questions before weighing the advantages and risks associated with Open Banking.
Open Banking as an initiative is being built to solve more than just few specific shortcomings faced by the consumer. Legacy institutions such as banks in India used to offer banking products that were built on very tightly built data and process systems that may have caused friction when customer tries to access certain banking services. Here are the few ways Open Banking bridges the gap between financial institutions and consumers.
How does Open Banking work?
To understand Open Banking, we need to begin with a basic understanding of API (Application Programming Interface) since it constitutes the core of Open Banking irrespective of the use case. In simple terms, API is a structured way for one software to communicate with another software.
In Open Banking initiative, the APIs are agreed upon by the stakeholders (Banks, Regulators, and Government) and the onus is placed upon the banks to implement them. The consumer data is acquired by the third-party from the banking institutions. This data is then used to build innovative products that ultimately benefits consumers, enterprises, or small businesses.
Open Banking- The Data in Detail.
Ease and convenience do not supersede security of highly sensitive consumer’s banking information. It is essential to understand the data that is accessed by third-party financial service providers and their purpose. The data is classified into three broad areas listed as follows:
1. Product Data- The products and services offered by a financial institution readily available online for customer’s perusal.
2. Account Data- It constitutes general bank account information such as Account Holder’s Name, Account Type, Transaction information, etc.
3. Payment Initiation- Transaction of money from one bank account to another. Open Banking simplifies and speeds up the online banking processes via use of software, apps, or websites with the consumer’s consent, eliminating the need for consumer to login and initiate a lengthy process for each payment or transaction.
What are the Benefits of Open Banking?
The Open Banking initiative provides secure access to data, the APIs as agreed upon by the stakeholders help create innovative financial products that benefit consumers, businesses, or financial institutions, offering convenience, cost reduction, personalisation, and improved decision-making. According to Statista, the number of Open Banking users worldwide is expected to grow at an average annual rate of nearly 50% between 2020 & 2024.
Consumer Benefits of Open Banking
1. Centralized access to Banking & Account Aggregation
2. Improved access & control of personal finances
3. Interactive & personalized Banking Experience
Business Benefits of Open Banking
1. Easy access to automation & innovative technology
2. Fewer barriers to entry for small businesses<
3. Higher competition guaranteed to improve banks’ offering
4. Increased customer engagement
5. Easier consumer credit risk analysis
6. Improved Resilience & Scalability
7. Favourable borrowing terms for small businesses
What are the risks associated with Open Banking?
As anticipated with implementation of any new technology in a legacy system, Open Banking faces several challenges. Here are the major risks perceived to be associated with Open Banking listed as follows:
1. Financial Privacy & Data Security- With increased access of personal information readily available for third-party apps, threat to data security- Cyber Security Risks loom over the innovation and creativity brought about by use of Open Banking. This amplifies the pressing need for consent and control of consumer data to be protected by privacy and data protection laws.
2. Customer Rights & Compliance- Customer Rights to Privacy of Data and Consent is incumbent to current regulatory actions. Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has issued Grievance Redressal System to protect customer interests and Right to Privacy ensures customer’s data remains private unless specific consent is acquired.
Open Banking Security Measures in India
With digitization of financial services and rise of FinTech, Government regulations being updated on a regular basis is hyper-focused on protecting consumer’s consent in data sharing. According to the RBI, the development of Open Banking in India is intended to be based upon a consent-based architecture with the following tenets:
1. Customer protection
2. Financial data integrity
3. Confidentiality
4. IT Governance and controls
5. Grievance redressal systems
Open banking is a potential disruptor in the financial and banking system. While resounding success of UPI (Unified Payments Interface), a payment system API for third-party apps and financial services providers to build upon, it is imperative to acknowledge consumer privacy is non-negotiable. It is the combined and consistent effort of FinTech sector, government regulators, and market participants that delivers a frictionless payment experience to the end-consumer.
Pay10 Payment Gateway is secured with PCI-DSS Level 1, SAR (PAPG & Data localization) and VSCC, ISO 9001:2015, 27001:2013 certifications. While the servers are hosted by reliable cloud service provider (AWS- Amazon Web Services) offering unparalleled data security, Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt information exchange, CoFT (Card on File Tokenization) implemented Payment ecosystem with enhanced checkout experience and strict in-house security guidelines that ensure confidentiality of payment information.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q1. What is Open Banking in simple terms?
- Open Banking or Open Bank Data provides third-party financial service providers with open access to consumer banking, transaction, and other financial data from banking institutions and non-banking financial entities via. (API) Application Programming Interface.
- Q2. Why do we need Open Banking?
- Open Banking enables and encourages development of innovative financial products that benefit the consumers, enterprises, and small businesses alike. Here are some of the broad benefits of Open Banking listed below:
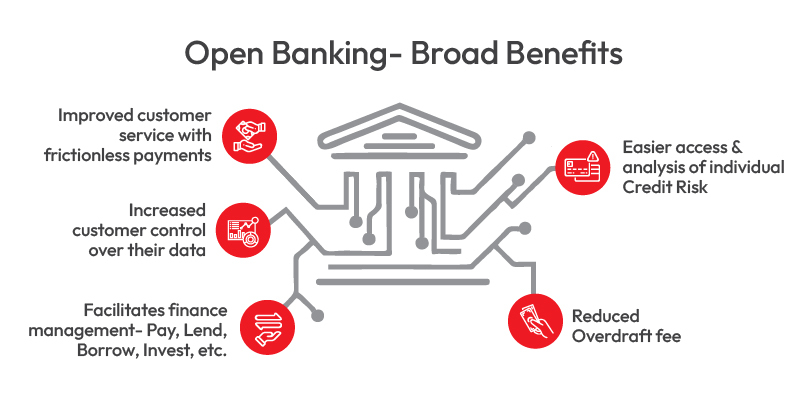
- Improved customer service with frictionless payments
- Increased customer control over their data
- Facilitates finance management- Pay, Lend, Borrow, Invest, etc.
- Easier access & analysis of individual Credit Risk
- Reduced Overdraft fee
- Open Banking enables and encourages development of innovative financial products that benefit the consumers, enterprises, and small businesses alike. Here are some of the broad benefits of Open Banking listed below: