5 Ways Fintech Bridges the Digital Divide in India
FinTech sector is a modern innovation that achieved the improbable- bringing previously under banked and unbanked sectors into the fold of organized sectors. The dramatic shift was fueled by several contributing factors including the sudden shift in consumer behavior during the Covid-19 pandemic. Although the innovations of FinTech sector have heralded a new age of cashless economy, the reality is profoundly farfetched for a sizable population living in the same country with internet penetration and supporting infrastructure being relatively sparse in the rural regions of India.
The digital divide in the country only widens with every innovation as the urban population have increased access to technology than their rural counterparts. As a deeply agrarian country, the rural population fuels the country’s growth and development. The digital divide limits the growth and opportunity that is afforded to the urban population. FinTech sector is equipped to serve as the uniting factor to bridge the digital divide in the country. Here are 5 ways the latest FinTech innovations can contribute to bridging the digital divide in India.
1. Direct Money Transfer (DMT)
Direct Money Transfer is an Agent Assisted Model that enables individuals to safely transfer cash to a beneficiary account. This FinTech innovation bolsters the rural and semi-urban demographic to access and easily connect with the new digital economy helping bridge the gap between the digital divide in India. The cash can either be routed either through NEFT or IMPS. The transfer is secure with dual authentication that requires both m-PIN and OTP that captures IP & location.

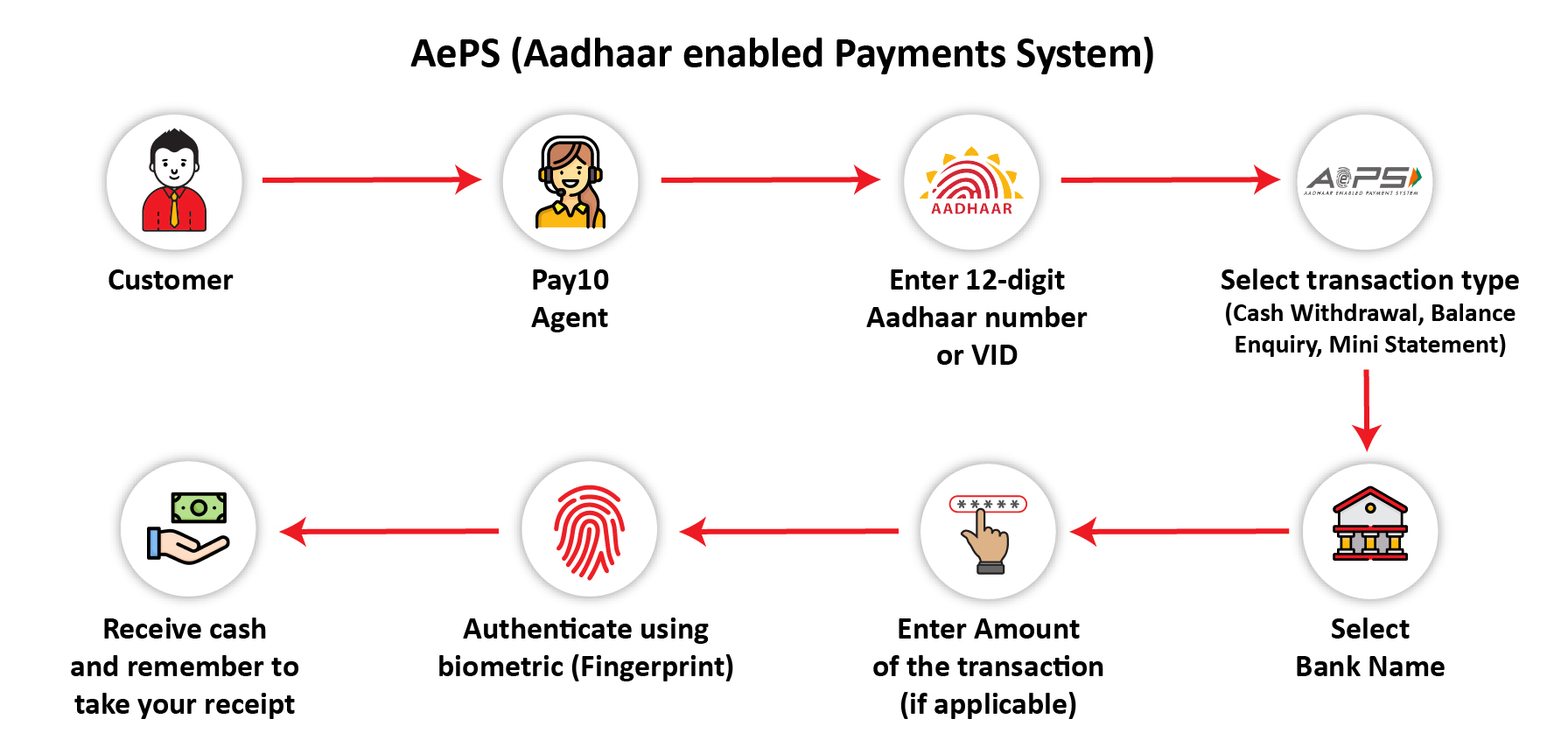
2. Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS)
Technology has percolated every industry with ever-increasing need of inter-dependance between different sectors for smooth and efficient functioning of any given system. With AePS, the customer can transfer funds, perform balance enquiry,and view mini statement using only their Aadhaar card that is linked to their existing bank account. The Agent Assisted Payment system is secured with Aadhaar masking and captures IP & location aiding in eliminating the risk of unauthorized access to the customer’s account.
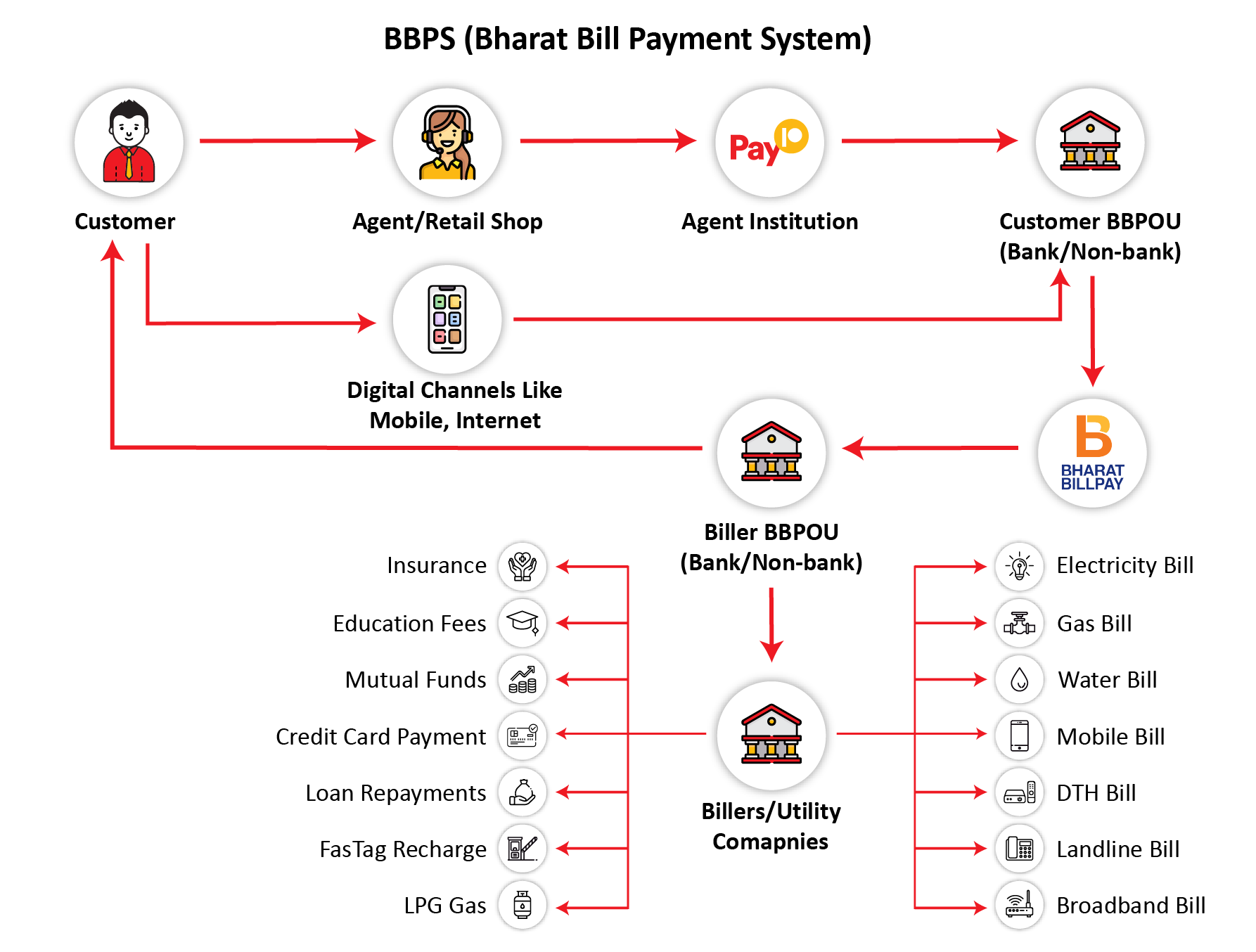
3. Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS)
The rapid development in technology has fueled every sector to adopt new innovations for easy and effective payment process. As several demographics choose to use digital means for paying bills for availing essential services, the rural segment is compelled to catch up to the existing pace of technological development. BBPS is an agent assisted Payment System that aids in paying bills for essential services such as electricity bill, water bill, DTH bill, Mobile bill, etc.
4. Micro-ATM
Cash withdrawal might have become a second nature to the urban demographic, but there are a few logistical challenges faced by the rural segment. The Micro-ATM is an agent assisted system that facilitates customers to withdraw cash and perform balance enquiry using Debit Card. The transaction is secured with Card Masking and captures IP & Location preventing risk of fraudulent transactions.

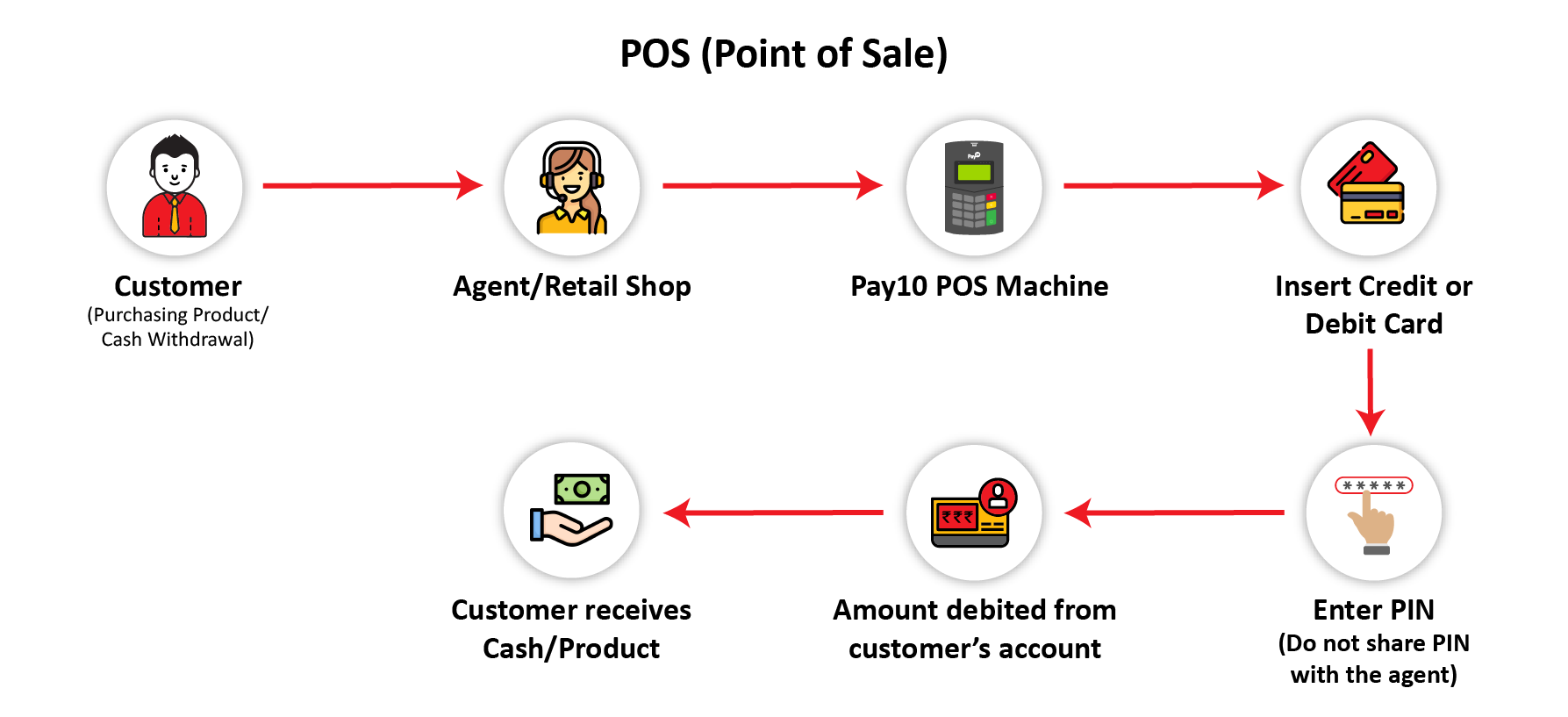
5. Point of Sale (PoS)
Retail and e-commerce sectors have advanced in leaps and bounds in the past decade with infusion of technology. Point of Sale is a Payment System that enables cash withdrawal or transaction using Debit/Credit Card. The Agent Assisted System allows customers to purchase products or services and withdraw cash using their Debit/Credit Card.
Pay10 is a Payment Service Provider keen to contribute to bridging the digital divide in India. Our innovative FinTech services are aimed at realizing the future of cashless digital economy in India that is inclusive of all demographics. You can take a look at our innovative and ultra-efficient Payment Gateway with reliable security features, supporting several payment modes, and powers an analytical dashboard; Payment Links, Billing service, Reseller services, Payout services, and more.

