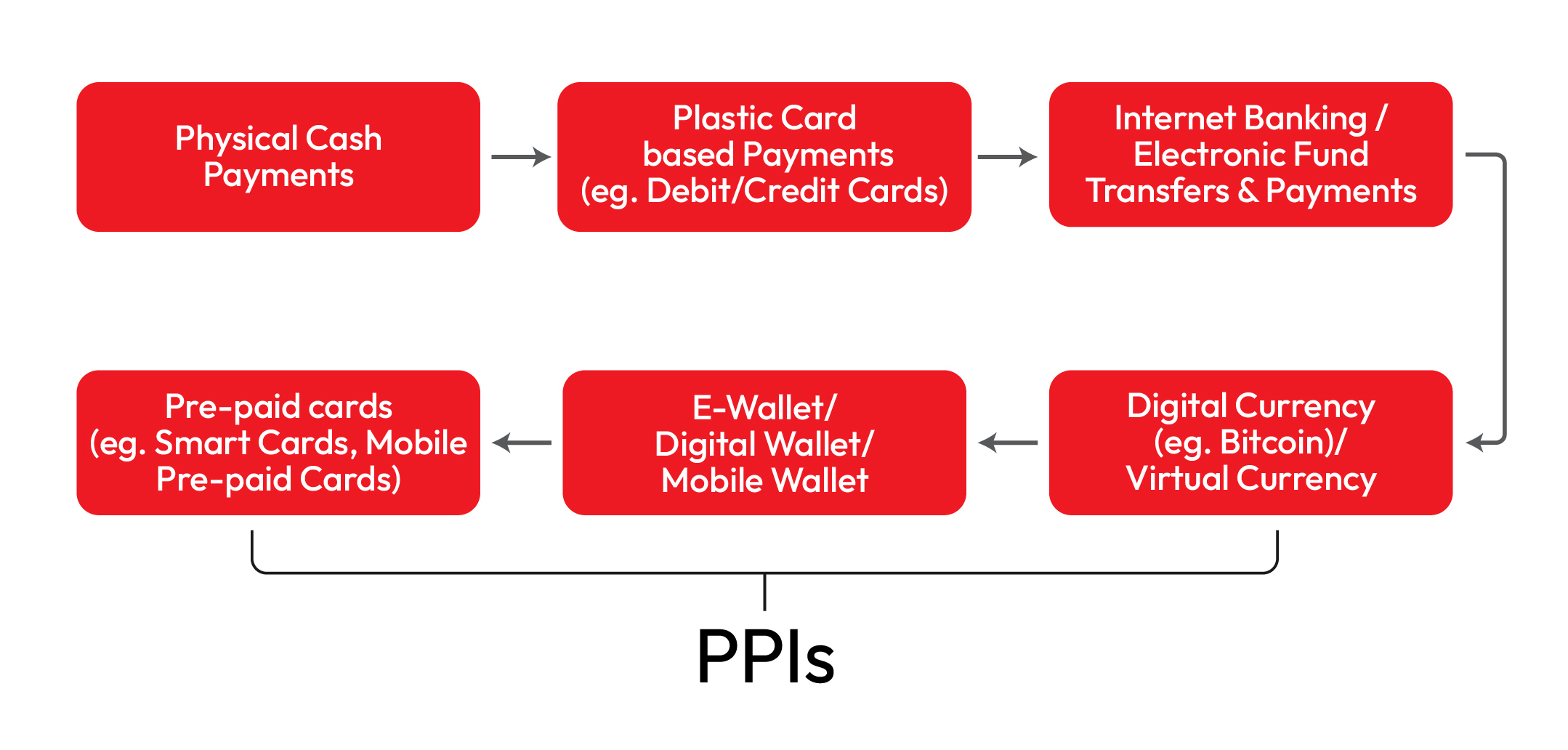
The Indian government has been driving the growth of digital payment in the country and demonetisation was one of the biggest initiatives that was taken to fuel payment digitisation. RBI has been diligently working on creating a robust electronic payment ecosystem however, the traditional payment methods are not given up completely,but digital payment instruments are widely being promoted for better customer experience. After demonetisation in 2016, PPIs grew up to 76.1 % in volume to INR 3459 million in FY 17- 18 and the value of PPI transactions rose to INR 1416.3 sbillion in FY 17-18 according to a report by PwC India. Let’s understand the basics of PPI through this complete guide to prepaid payment instruments
What is a “Prepaid payment Instrument”?
Prepaid Payment instruments, also known as stored value cards, facilitate the purchase of goods and services against the value stored in them. The value stored on the card represents the money that has already been paid, by the cardholders in advance, through cash or debit/credit card. There are many variants of PPIs, ranging from smart cards, mobile wallets, and coupons/Vouchers, however, all these cards have different features attached to them.
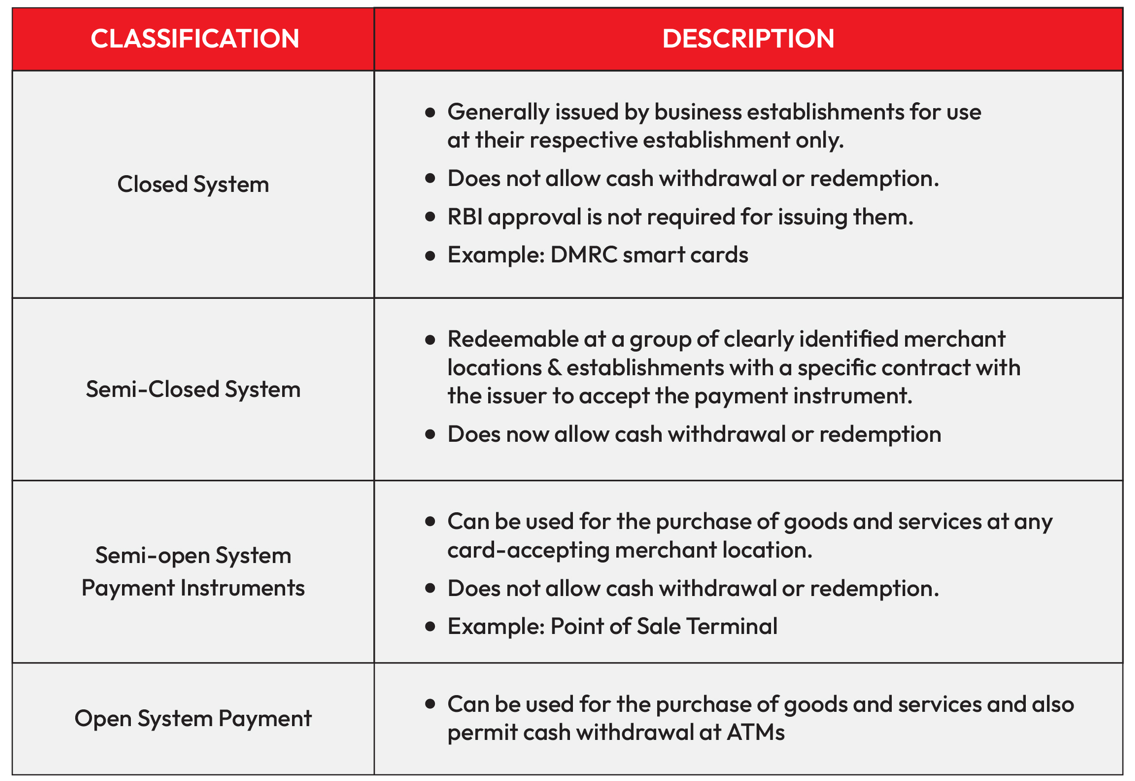
Types of Prepaid Payment Instruments
Prepaid Payment Instruments are generally issued by banks or non-banks where financial institutions need to take approval, and non-banks need authorisation before issuing such PPIs.
There are 4 types of PPIs based on the classification of their features.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Prepaid Payment Instruments
Prepaid Payment instruments can be conveniently used in the form of digital wallets, physical coupons or physical cards just like traditional credit/debit cards. There are various benefits of keeping PPI cards, as the holder does not have to stand in long queues for tickets as these cards are commonly used by mass transit system operators. Issuers also offer promotional benefits a PPI user gets.
Advantages of PPI
1. Minimum Formalities
2. Convenient
3. Saves Time
4. No Possibility to Get into Debt
5. Controls Spending Habits
6. No Need to Carry Cash
7. Promotional Offers
Just like the two faces of the coin, along with many advantages, there are a few disadvantages of the Prepaid payment instrument. These cards can be loaded with money for further use, but are not linked directly to any bank account, thus the security threat increases.
Limitations
1. Not Linked to any Bank Account
2. Can not be used as Credit Card
3. Security Threat
4. Additional Fees
Who Can Issue PPIs?
Banks in compliance with the eligibility criteria issued by RBI shall be permitted to issue PPI. According to RBIs Master Direction Banks, seeking approval from the RBI under the PSS Act shall apply to the Department of Payment and Settlement Systems (DPSS), Central Office (CO), RBI, Mumbai along with a ‘No Objection Certificate’ from their regulatory department, within 30 days of obtaining such clearance.
All the non-bank entities seeking authorisation from RBI must be incorporated in India and registered under the Companies Act 1956 / 2013. Companies seeking authorisation under PSS Act shall have a minimum positive net worth of Rs.5 crore as per the latest audited balance sheet. Also, by the end of the third financial year from the date of receiving final authorisation, the minimum positive net worth of Rs.15 crore should be achieved and shall be always maintained.
What is PPI Interoperability?
Interoperability is tech compatibility that enables devices, software and products to connect in a coordinated way. In PPI interoperability, one payment system operates in conjunction and coordination with another payment system(s). With a vision to enable PPIs to become an integral part of the larger financial services ecosystem, RBI issued its much-anticipated directions on interoperability for PPIs on 16 October 2018. Under this, many PPI issuers, tied up with the National Payments Corporation of India for issuing Interoperable RuPay PPI cards or creating interoperable wallets on UPI rails. PPI interoperability through UPI has been a crucial step for speeding the growth of merchant transactions in rural areas and further deepening financial inclusion. It will further help in boosting the universal acceptance of wallets across all UPI QR codes and devices.
Future of PPIs in India
It is a fact undeterred that the 2016 demonetisation has given digital modes of payment an unexpected stimulus. However, the consistent growth highlights the acceptance of online transactions amongst Indians. There are a considerable number of factors behind the accelerating growth rate including different variants of prepaid payment instruments.
1. Traditional bank transactions and ATM withdrawals are becoming costly with levied charges. On the contrary, PPIs and digital modes are ushering in additional benefits such as discounts, cash back or reward points.
2. The digital ecosystem in India is taking an impressive turn given the internet penetration in the remotest areas of the nation conducive to a robust environment for the growth of digital payment modes including PPIs
3. For the past few years, smartphone penetration is also taking place at a remarkable pace, and undeniably the growth of PPIs issued on electronic formats is primarily dependent on the number of smartphone users. The usage and availability of tech support are enhancing the adoption of PPIs
4. The government has been taking numerous initiatives for digital inclusion, reducing the gap between India and Bharat. The growing awareness of digitisation in the rural demographics has made digital payment instruments acceptable to India’s rural population.
5. Opening and operating a semi-closed system PPI account is relatively easier as compared to opening even a basic service savings account. This gives PPIs an edge over traditional bank accounts and associated digital modes like debit/credit cards and net banking.
Prepaid payment instruments aid in simplifying business operations for higher scalability and growth in the venture. This elaborative and complete guide on prepaid payment instruments will hopefully help you take a sound decision. If you are struggling to find a reliable payment gateway for your business, feel free to connect with us. Pay10 is a multifaceted payment gateway offering hassle-free merchant onboarding with zero set-up and integration costs. The ultra-efficient payment platform is equipped with a fully analytical dashboard and offers world-class security features supporting 100+ modes of payment including e-wallets and UPI facilities.